Semester7
Notes of courses done/attended in semester 7 in college
Lecture 6
Video
link
Slides
link
Paper
Agenda
NDN Architecture
- communication is driven by the receiver(consumer)
- sends interest packet
- eg
/pilani/computerscience/courses/acn/lectures/lec1.pdf
- focus is on what instead of where
- Router forwards Interest packet by looking up the name in its FIB(Forwarding Informaiton Base) (name based routing protocol)
- FIB is similar to routing table
- Data packet travels on the same path followed by Interest packet in reverse direction
- it carries both the name and the content of the data, together with a signature by the producer’s key
- Packets formats

- nonce = randomly generated fields
- signature = data is authorized by producer
- in signed info, I can also specify if data is cacheable or not, or give some TTL value for caching
- Request and response
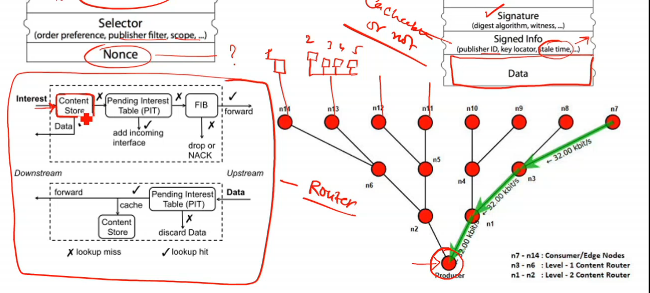
- on left is a complete router u can say
- PIT table = store interest references
- interest = query, what user wants to access
- when a req comes, if the request is already in the PIT table, I just add into PT table a new interface (incoming interface), bcz request already ja chuki hai
- else, if not present, I add a new entry and interface and send request to FIB
- FIB checks ki next interface kya hai jaha it should send request, and accordingly it forwards to an interface
- similar actions happen at other routers
- now req reaches producer, it sends response
- router ne kaha resp aya mtlb pit e entry toh hogi hi, so Pit me dekha and interface nikala and removed entry from its table and us interface(s) pe bhej di file
- so same path is being followed in reverse direction
- if pit me entry nahi hai, then it will discard the data
- when it is possible?
- maybe malfunctioning ho gayi ho kuch
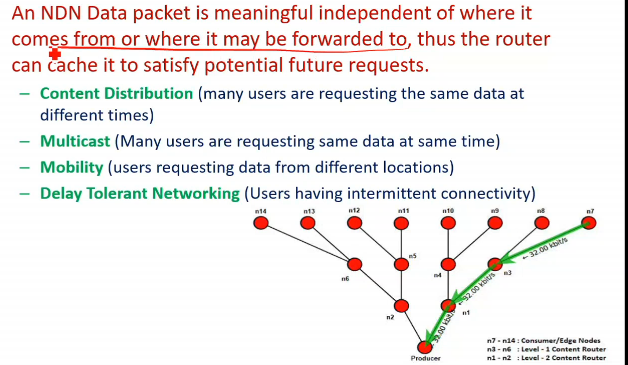
- all nodes(routers) in path act as content store, and hence store the file
- if a new request comes to one of the store, It sees ki bhai data already available hai iske pas, so yehi return kardega, producer ke pas nahi jayegi request
- so if smth is more popular and being used, it will be replicated in the n/w automatically, CDN nahi use karna pad raha jo internet me karta
- baki kab delete karunga is evicting policies, TTL and all
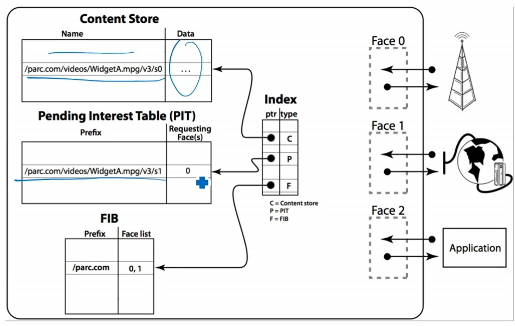
Data Names
- how to find the data, or how the data are named and organized to ensure fast lookup and delivery
- hierarchally structured names
/pilani/computerscience/courses/acn/lectures/lec1.mp4/1/2- names are appln specific and opaque to the n/w
- dynamic data can be retieved by common agreement b/w consumer nd producer
- not all the names need to be globally unique
- name space mgmt is not part of the NDN arch, just as IP address mgmt in IP n/w
Data Centric Security
- secures data dirctly instead of securing the data containers such as files, hosts and nw connections
- each pice of data is signed (mandatory) together with its name, securely binding them
- NDN’s data-centric security can be extended to content access control and infra security
Routing and Forwarding

- in IP arch, routing and f/wing planes are coupled
- they say, routing can independently work
- routing provides multiple paths, and f/wing decides what to pick
- but IP me, routing plane provides single shortest path, (shortest depends upon how u define cost, min hops, min b/w etc)
- main same idea use kar sakta, prefix vs interface mapping, bas prefix will be acc to name
- but yaha pe name length pe toh koi limit nahi, IP me toh thi
- so how to scale? how to store and search efficiently

- ndn supports multipath routing
- no chance of looping like IP routing
- it improves routing security as well

- particular machine cannot be targeted bcz there is no concept of address
- so this type of DOS attack is not possible
- but we can do content based attack, target some content, but bahut content-distributor ban chuke hongey, so severe nahi yeh
- Privacy protection
- no info about who requested what data

1resareas
Resources








