Lecture 8
Video
Slides
Reference
Agenda

SDN: Network Virtualization
- decouples control and data plane
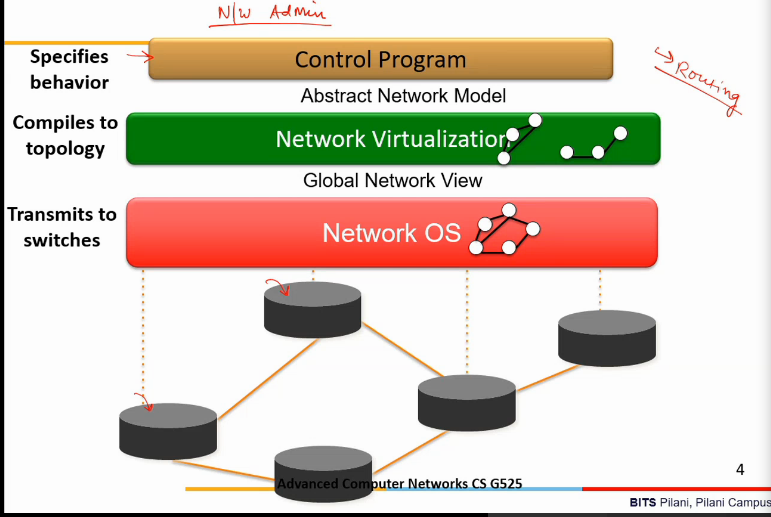
- control removed from each individual switch
- What does network admin gets
- an abstract view in form of virtualized n/w
- virtualization achieved by abstraction
- can control and manage the n/w
- can specify behavior in term of control program
- routing kaise hoga bata sakta
- access control list
- who can control to whom
- maybe ek server kuch hi end points se access karwana
- traffic engineering rules
- specify a QoS requirement by applications
- some apps require more b/w
- some require least latency path
- path provisions to the apps is done here
- for diff flow of packets diff provisions
- specify a QoS requirement by applications
- all these are specified using a progrmming interface
- then pass it to virtualized view of n/w
- which then compiles topology on these rules
- validates ki everyth is fine or not
- all req are done or not
- then push through n/w os into each switch
- We can achieve all these things in legacy n/w also but it is a tedious task
- centralized view of n/w construct karna padega khud se
- and validation part nahi hai, so directly install kardo and bug ho toh resolve karo
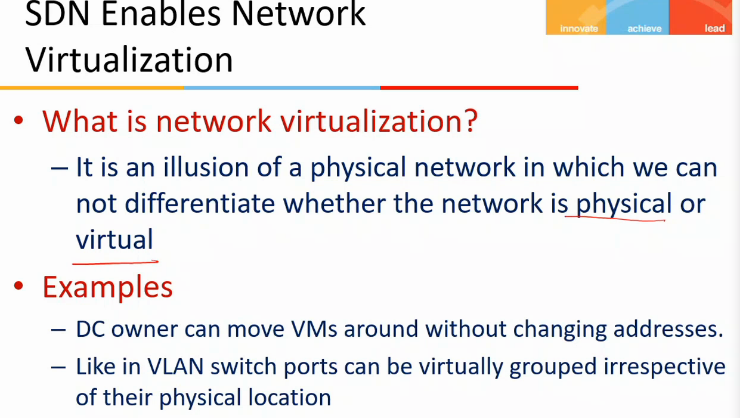
- eg
- data center can move any machine w/o changing addressing space
- in VLAN, switch ports can be virtually grouped irrespective of the physical location
- machine in FD1 can be put in VLAN with machines in FD2
Abstractions in Computer Systems

- apps do not worry about managing physical locations and caches, through virtu it gets infi phys memory
- file system = os provides it
- h/w me kaise data store ho ra, sector, tracks and all Idc
- VM = os abstraction
- app do not have to worryr abt new process scheduling and all
Does SDN Simplify the network
- abstraction does not eliminate the complexity
- everything is still happening
- but OS karra woh jaise file system me
- Network Operating System karra yaha
- so programmer ko nahi dekhna kya hora
- SDN main achievements
- simplifies interface for control program(usere-specific)
- pushed complexity into reusable code(SDN platform)
- it works just like compilers
- compiler abstracts the details
Centralized vs Distributed Control
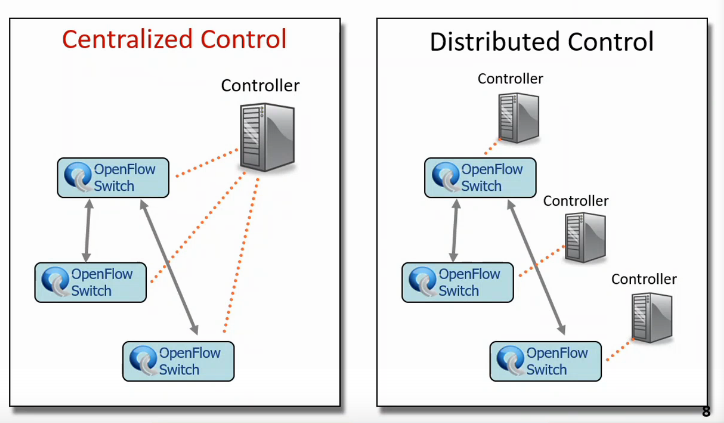
- Single Point of Failure nahi ab
- to get consistent view(if reqd), they will communicate
- this is East-West bound interface
- communication b/w controllers
- OpenFlow
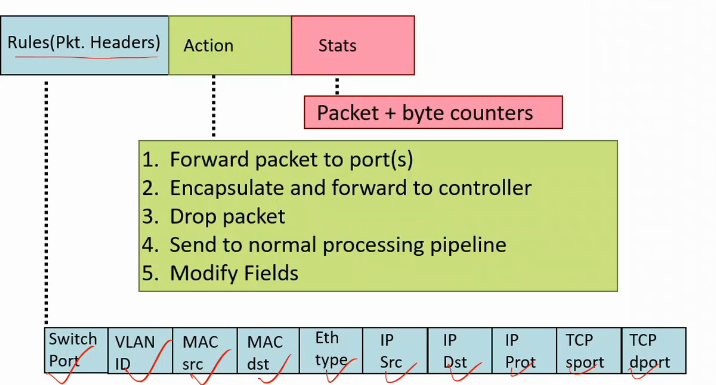
OpenFlow v.1.0 switch
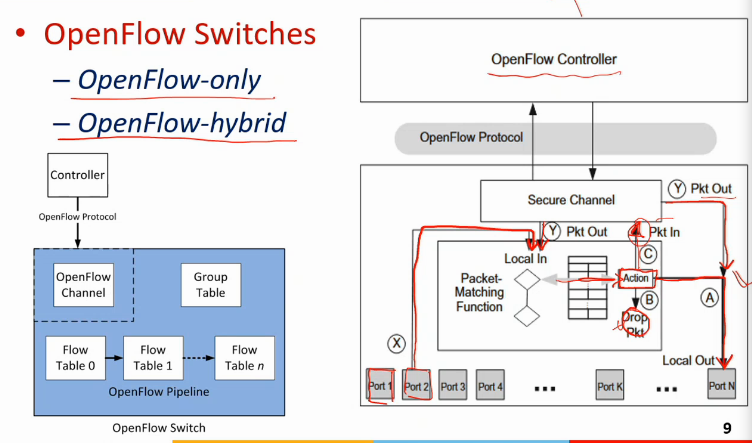
- a new pkt arrives at a port
- flow table is maintained
- rules hai isme
- controller se aaye rules
- controller ko n/w programmer ne die
- if no rule is matching, pkt sent to controller through a secure channel
- controller pushes a rule based on criteria set by n/w admin
- either controller can find out action for that
- action = what is to be done with the pkt
- drop it, or send to diff port
- either he sends directly to that
- action = what is to be done with the pkt
-
a pkt which came first time will be sent to controller
- Switches are of 2 types
- openflow-only
- all switches are o/f only
- openflow-hybrid
- kuch traditional switches and kuch o/f
- halke halke I will change
- openflow-only
- there could me multiple flow tables
- chained together, they act like filters
- say 1st table does firewall operations, then 2nd does layer3 operns, then 3rd table layer 2 operns
- table size will be less
- a special table = group table
- used to group the flows
- say some common action on some flows
- like sab kuch ISP ko bhejna
- multicast/broadcast karna
Openflow Controller

- traditional switch bahut kuch kam karre so complicated
- they also have data and ctrl planes
- so how SDN wala is different
- are decoupled hai na bhai
- SDN control plane is centralized view but usme distributed
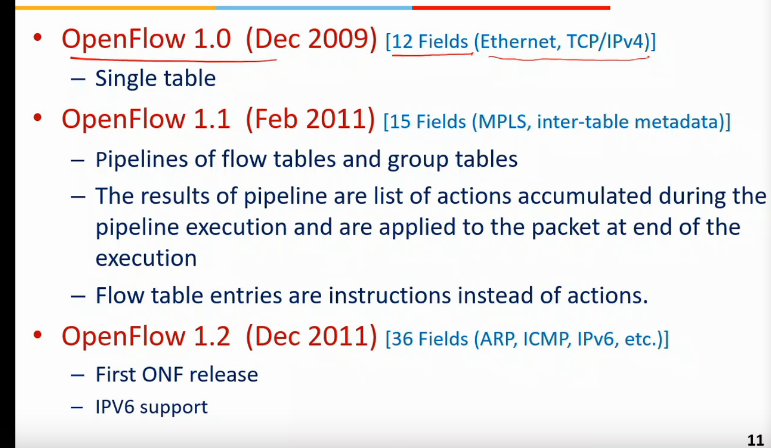
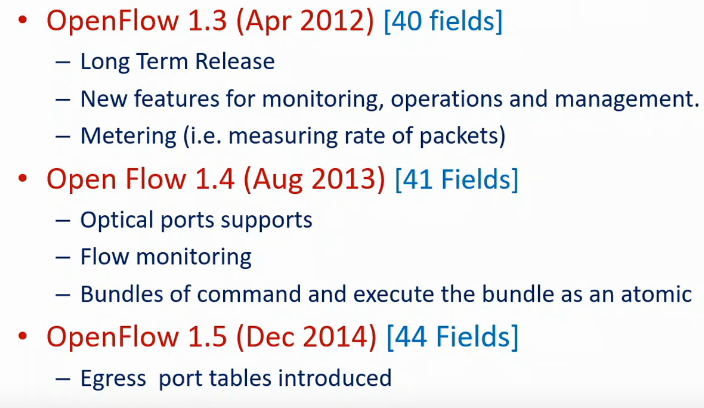
Openflow specs
Openflow ports
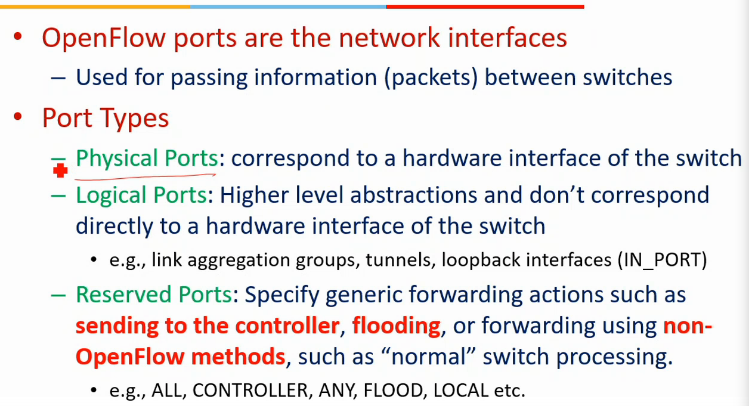
- physical
- one-to-one mapping
- logical
- reserved
- spl meaning
Rserved ports
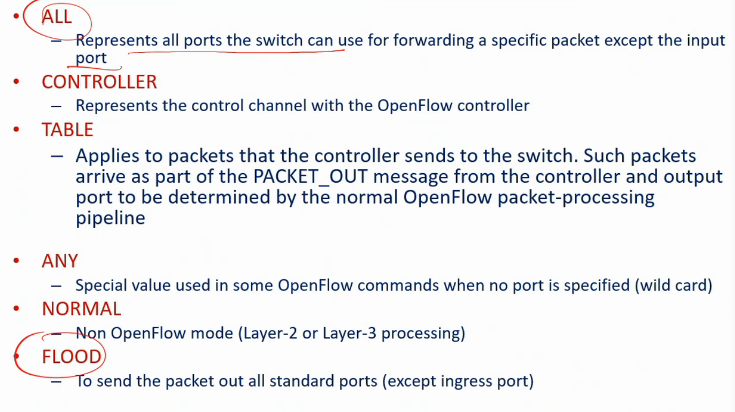
Flow Table