Semester7
Notes of courses done/attended in semester 7 in college
Lecture 23
Data Replication
- have copy of data at multiple places
- advantages
- increase availability = fault tolerance
- distributes load among multiple nodes
- decreases latency, ppl send request to node close to their system
- Challenges
- any change in one replica , must be refglected in others else inconsistent states, this s synchronous replication
- this affects latency
- Asynchronous replication
- keval ek me kar abhi, baaki ka asynchronously hota rahega
- 3 kind of replication strategies
- single leader
- multiple leader
- leaderless

Leaderless replication
- there is no ordering of requests
- when leader is there , one replica is primary and others are secondary
- secondary do not accept request for update, only for reads
- for any update to be done, they send to primary or client sends to primry
- primary applies writes in some order and also tells to secondary ki is order me lagayo, so all of them see same state
- here, no leader
- client can talk to any replica for r/w

- DynamoDB is based on this
- S3 is built on top of Dynamo
- dynamo is very much scalable
Read and Write in Dynamo-Style DBs
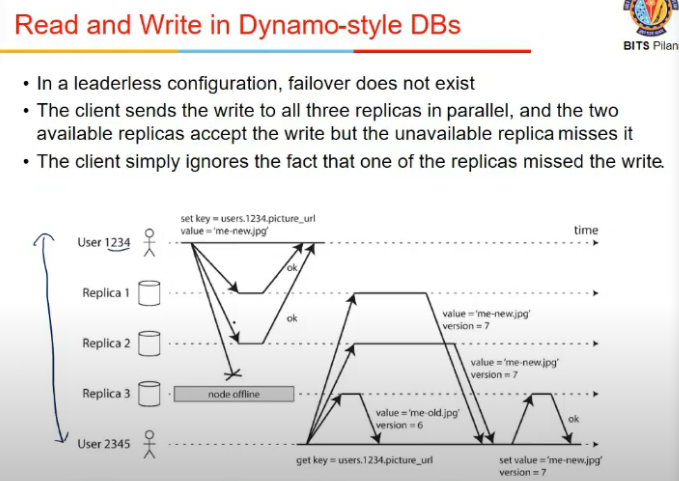
- 3 replicas and 2 users
- user 1234 is updating, updating in all 3 replicas
- 1 replica is offline
- so bas 2 me changes hue
- user 2345 asks for image url
- 2 nodes give same info, 3rd node gives diff
- he sees ki 2 node me new version so tells last node to correct it
- so, read requests must be sent to all the replicas and update stale values
Read Repair and Anti-entropy
- when u read, read from all and update if needed
- it may not give update to db easily, bcz reads may not be frequent
- so anti-entropy process
- bg me chalta and checks if some older version remains etc

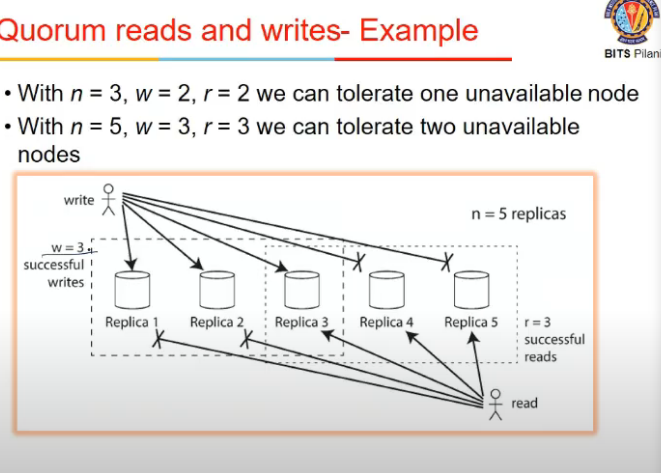
Quorums for Reading and Writing

- Does read have to be from everyone?
- nah, follow quorum principle
- when we write, say there are n replicas
- we write to w nodes, and read from r nodes, such that w + r > n
- the idea is the nodes in which we write and from where we read must overlap (atleast one node must be part of overlapping region)
- so atleast one ndoe will have value of most recent write
- r and w can be chosen, n is fixed

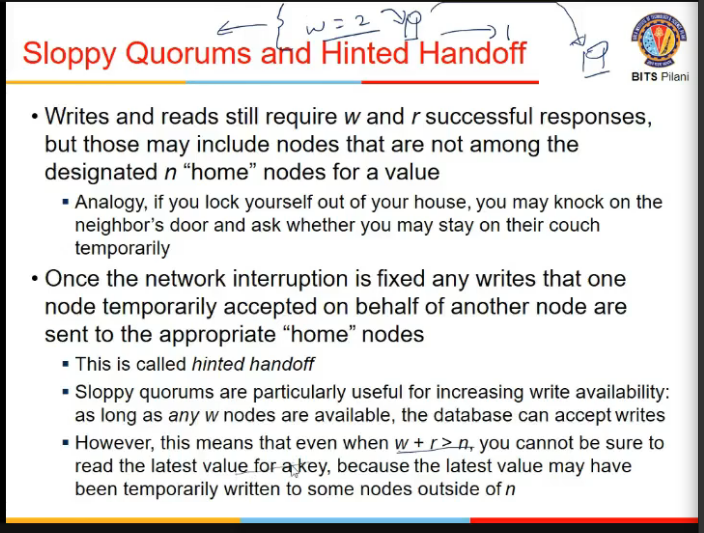
Sloppy Quorums and Hintend Handoff
- specific to dynamo
- sloppy quorum
- say write quorum is 2, but u can write only to 1, so it makes an intermediate node and write there, and sayas all is ok
- tho it has not written to actual node
- when node comes online, value is copied to the node which is back
- when u read, are proxy/temporary used?, don’t know. they might not, so inconsistency might be therw
- tradeoff with performance
Limitations of Quorum reads and writes
- is it sufficient to follow quorum to ensure everything is ok?

Detecting Concurrent Writes
- a data item being written by 2 diff client in 2 diff replicas

- version number diff nahi, ambiguous hai version number
- detect using version vectors
Version Vectors
- for each data item, keep a version vector along all nodes
- position in vector correspond to node number
- all elems in one vector < second vector then ok,
- 100 < 200, 100 < 110
- but if some value is smaller, some are larger => concurrent writes ho rahe
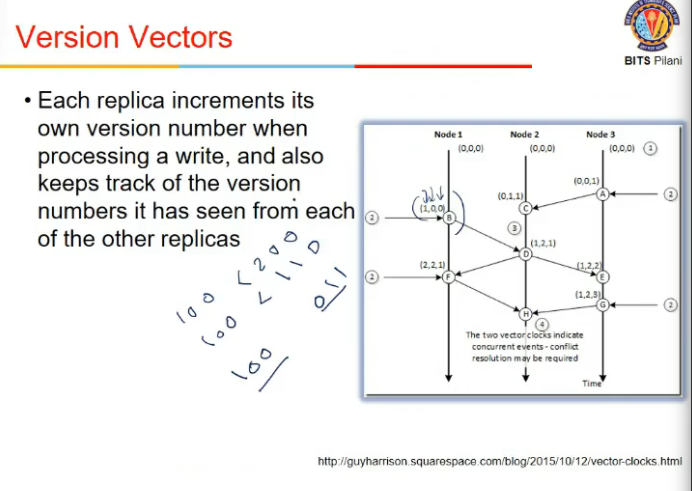
- if conflict hua, what is considered as most recent
- Last Write Wins
- timestamp for every write, latest timestamp wala le le, baki ko reject
- achieves eventual convergence, but durability ke cost pe

Capturing the Happens-before == Causal relationship
- which one comes first, which one comes second etc
- server can determine if 2 operns are concurrent by looking at version numbers
- maintains version number for each data item
- value written to key => increase version number
- when client reads a data item, server returns all versions
- b4 writing client must read all values
- so write is not successful unless we read all values
- when client writes a key, it must include version number from previous ones
- overwrite all versions less than what client has told. higher waale rakhe rteh as at is
Merging Concurrently written values
- requires application semantics
- union for a shopping cart
- 2 alag entries aayi, merge kardia unko
- last write wins
- what number of minimium and max nodes can fail (how robustly I handle it) depends upon quorum values











