Lecture 24
Data Partitioning
- duplication of data nahi hai
- one big data stored at multiple places splitting it
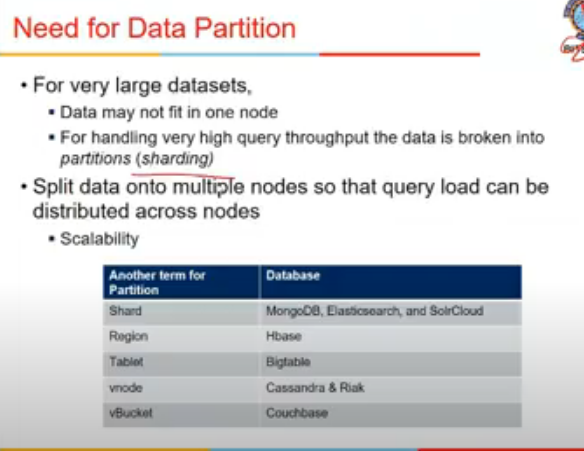
- this concepot is sharding
- known as shard in MangoDB, Region in Hbase, etc etc
-
data partitioning and replication could happen simultaneously
- each piece of data (row) belongs to exactly one partition (horizontally partition hai), fields are not split
- instance of fields store at diff

- diff b/w HDFS and partitioning?
- hadoop is file wise while others are wrt rows and columns
- hadoop me bhi partitioning hai but file ke terms me
- db me rows/documents ke terms me hai
- hadoop me we have replication as well along with partitioning

- Purpose?
- load balancing
- so that hotspot na ban jaye ek node
- How to partition data
- sorting
- hashing
- randomly distribute the keys
- retrieval is difficult
- query should be efficient
- Two types of query (in gen 2 types)
- Equality
select * from table where column = value
- Range query
select * from table where column > value
- Equality
Approaches to partitioning
- Key range partitioning
- we have range
- sort data by key
- b/w value a and b, go to node 1
- b/w value b and c , go to node 2 and so on
- range queries efficient since sorted order hai
- there can be hotspots, key accesses more frequently might be in closer range

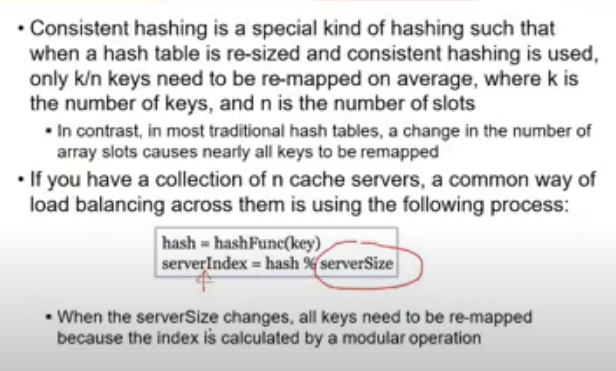
- Hash partitioning
- appl hash function to key, it gives a node # where to go
- range queries are diff

- How to repartition when there is imbalance? new node added, removed etc
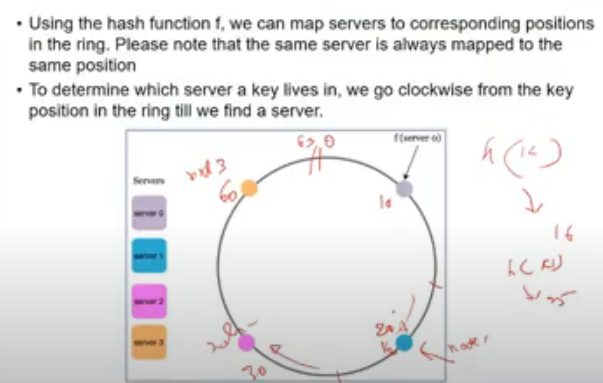
Consistent Hashing
- we have a set of nodes and key space(0..2^4-1)
- node joins the n/w, it is hashed using hash fn
- when key is hashed, it also lies somewhere in that range
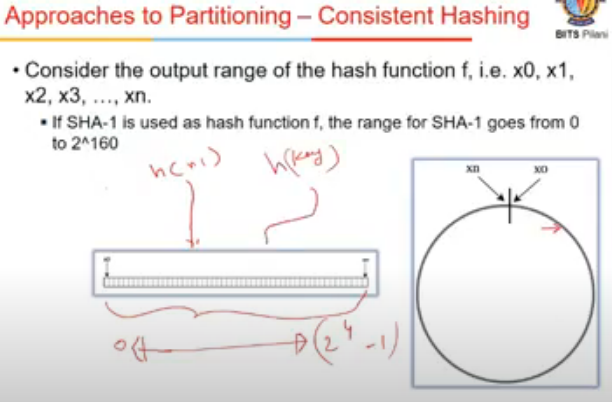
- I take key and hash it, it gives me some number
- key ke hash maan 16 pe aaya and waha koi node hi nahi, so usko next node pe laga de
- next server in clockwise dirn wala utha leta hai
- advantage?
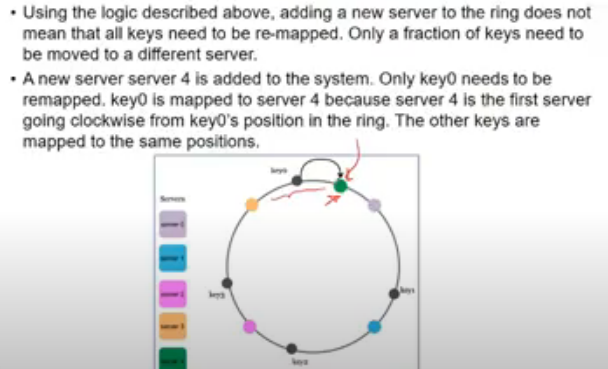
- new server (green wala) is added
- initially key 0 was mapped to gray node
- now keys b/w yellow and green jo thi, woh pehle grey pe mapped the, ab green pe ho gaye
- so only some keys need to be remapped
- if a server is removed(fails down), key mapped to next server

- load imbalance ki prob a sakti
- key space b/w 2 servers is non-uniform
- so how to work it out
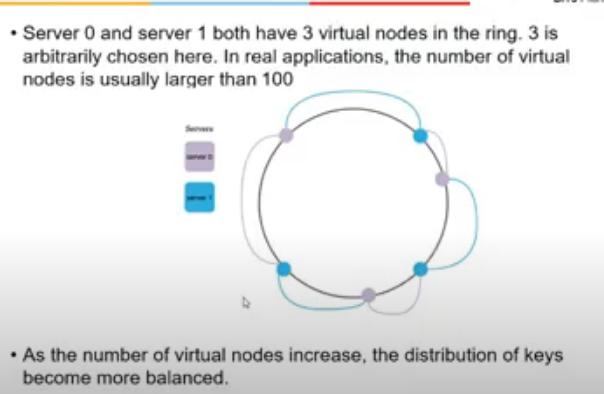
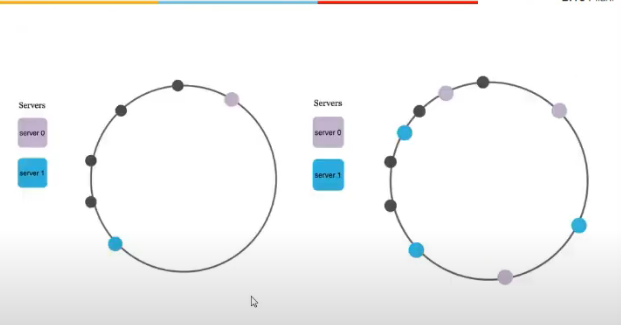
- add a virtual node
- node actually does not exist
- same physical server is added virtually as multiple physical servers
- sorting and hashing dekh li
- hashing me equal queries efficient
Hybrid
- Cassandra uses this approach
- sorting + hashing
- key is based on multiple columns
- first part is hashed
- others are sorted
- within partition how to search out, is using sorting
- one-to-many relationship hai agar, student id is repeated in every part na, so usko hash karke partiion nikal and then within partition it is sorted and hence searching easier

Skewed Workloads and Relieving Hot spots
- even though equally distributed hai data, hotspots still can occur

- one of way is while writing, same key add smth more to it
- to divert read and writes for a givem key using a random number
- if a key is hotspot, add some random integer , it will become new key , and it goes to diff partiion now.

Secondary Indexes
- not unique but still mnight help in search

- 2 approaches to maintain 2ary indexes(everything is not in one partition na bcz partiioning isbased on primary key)
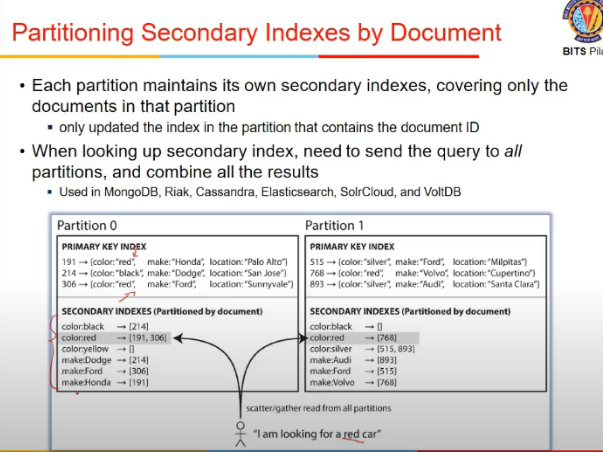
- document based partitioning
- within partiion, create a 2ary index
- execute query across all partitions and combine results
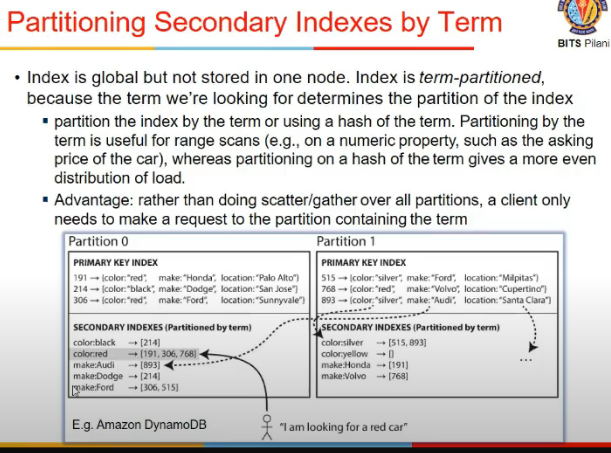
- term-based partiioning
- or, create a global index
- multiple partiions me query nahi karna
- jaha jaha pe data hai, wahi pe query kar
- document based partitioning
Rebalancing Partitions
- kind of load balancing
- queries ko proper response time mile
- moving data in cluster from one node to other
How to do
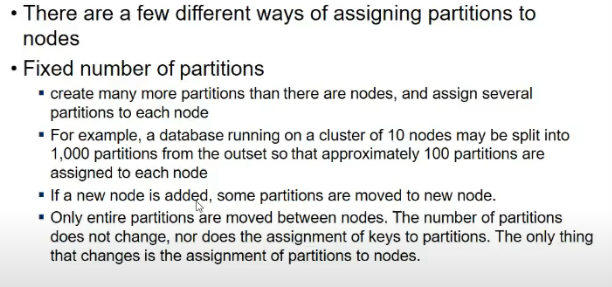
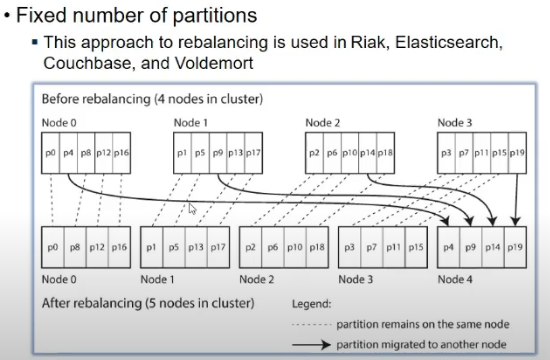
- Fixed number of partitions
- say 1000 partitions the
- every time node added, partition moved to node
- #partitions remains ame, size may vary
- Dynamic partitioning
- key range partitioning
- sorting of keys se ja raha
- fixing number of partitions is diff
- idk how many values will be there within a range
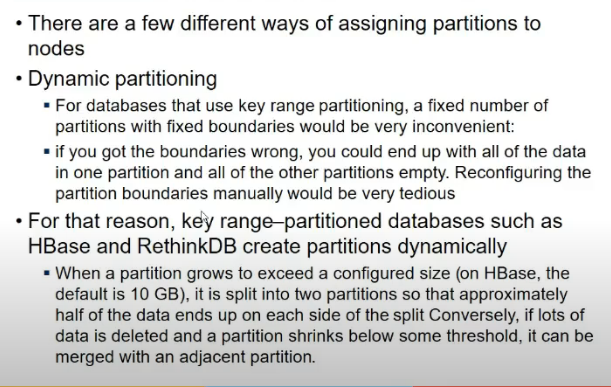
- indynamic, number of partitions are proportional to data size
- in orher approach, har node ko fixed number of partions de de
- when partition size increases split it

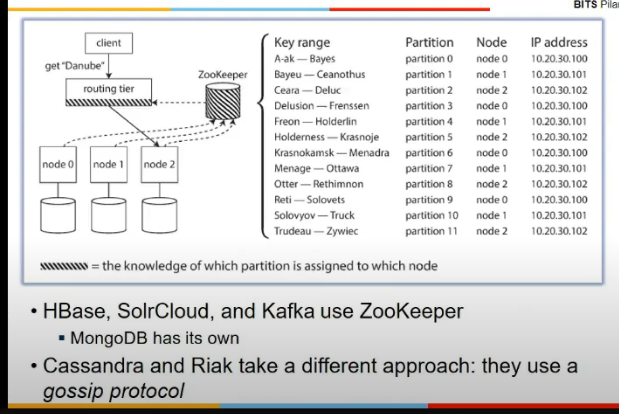
Request routing
- end user does not know kaha data lies

- diff approaches
- first
- dns based thing
- allow client to communicate to any node
- if node contains partition, it answers query else send to respective partition
- second
- send all request to router and it will handle where to send
- first

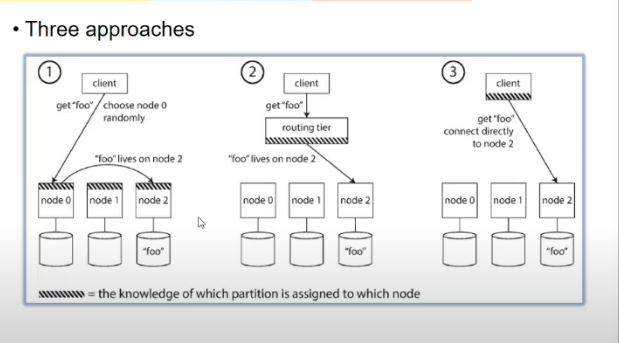
-
dotted are devices whiuch need to know where data is there
- third approach me client ko hi pata kaha pe bhejni
- how component making router decision comes to know about changes made in partiion node mapping
- many distrbuted systems depend on service like zookeeper
- allows multiple nodes to write
- and ensures consistency bani rahe
- notifications bhej dega subscriber ko
- stores all mappings