Lecture 31
Resource Management in VMM
Shares vs Working sets
- OS me working set model hota, kya pages abhi being used
- in cloud, we have to also see Vm level promises we make
- importance, ownership, amount of money paid to service provider for executing the vm
- penalize less imp bm, even if it would derive largest perf benefit from additional memory
Share based allocation
- give resources acc to shares that is held by vm
- share is regulated parameter
- client consumes resources proportional to its share
-
guarantted min resource fraction equal to fraction of its total shares in system
- algorithms for proportional share
- dynamic min-funding revocation algo
- revoke memory from client that owns fewest shares per allocated page
- take memory away from those payingh lower price to those willing to pay higher price
VMWare ESX - Share based allocation

- always not feasible
- might be ki higher ratio wala having larger #pages, ab woh use karra ki nahi idk
-
idle memory tax
- prob with pure proportional share allocn
- idle VMs with many shares can hoard memory unproductively
- active vms with few shares suffer under memory pressure
- resolve this by introducing idle memory tax
- fraction of pages being utilized and idle nikal le
- f = fraction of number of pages which r active (say 10 me se 5 hi active => 0.5)
- cost is k = (1/(1-t)), t = tax
- if t = 0, same as min-funding algo = S/P
- t defaults to 0.75
- cost we r imposing on system with idle pages
- penalizing not utilized pages
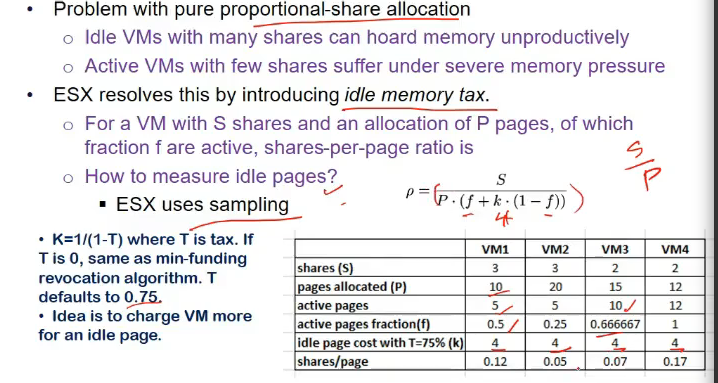
- jiske pas extra tha usse le lia, and jiske pas nahi tha, usko de dia
Resouce allocation policies
- 3 parameters
- min
- min this should be avaialnle so it can run
- max
- amount of physical memory configured for use by guest os
- shares
- entitle vm to fraction of physical memory based on proportional share allocation policy
- min
- Admission control
- a vm is admitted if min+overhead(for page tables, shadow page tables + grpahics grame buffer) is available
- max-min swap space honi chahiye
- tabhi take this vm into ur system
- ESX dynamically computes memory allocations and reclaims memory when below threshold
- 4 memory thresholds
- high
- no reclamation
- agar free memory available is only 6%, then lio
- soft
- use ballooning to reclaim
- free% = 4% pe
- hard
- forcible paging
- 2%
- low
- stop execution of vms reclaim pages
- 1%
- high
- 4 memory thresholds
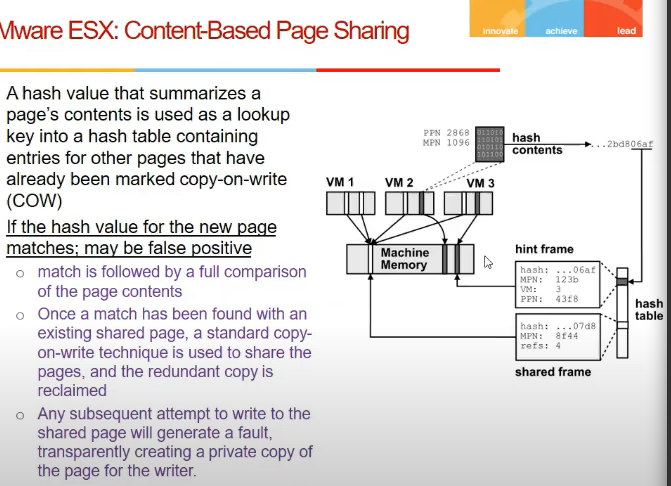
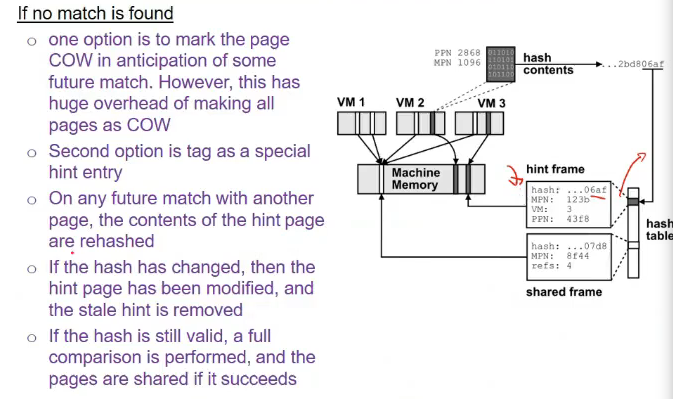
Sharing MEmory across VMs
- if 2 processes using same code, say vi editor, os only creates one copy and maps to the process executing
- esx bhi aisa kuch karta
- say 3 vms hai, 2 runnign windows, 1 running linux
- if 2 vms use same pages.. how does it know?
- hashing technique use karle
- and idea laga ki agar same pages acces kar rahe 2 machine
- if changes kie kisi ne, then copy karde(copy on write policy)

Resource mgmt - local vs global
- optimizing reosource mmgmt at vmm level(locally)
- but it might not globally lead to optimal resource mgmt
- cloud me globally chahiye bhai
- 2 parameters that paly role in dynamic resource mgmt
- perf
- energy efficiency
- vm migration
- perf
- why imp to look globally?
- even if har vm khud se acha karri, it might be underloaded, vms might be able to consolidated
Borg system
- cluster manager used by google for admitting, scheduling, starting, restarting and monitoring jobs
Architecture
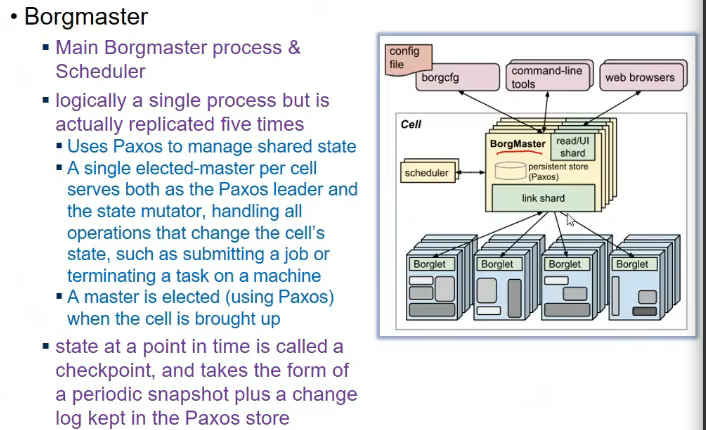
- borg cell
- set of machines
- a borgmaster
- logically centralized controller
- an agent process = borglet
- runs on each machine
- gives info to server
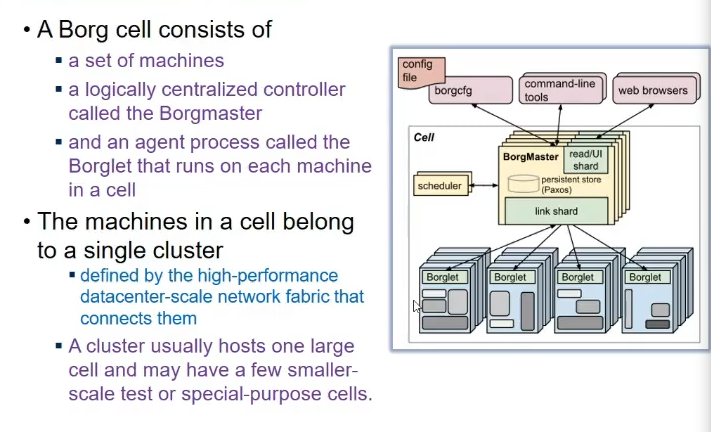
- machines in a cell belong to single cluster
- cluster usually hosts one large cell and may have smaller scale test or special purpose cells
Borgmaster
- schedules jobs submitted to it
- logically a single process but is actually replicaated 5 times
- uses paxos to manage shared state
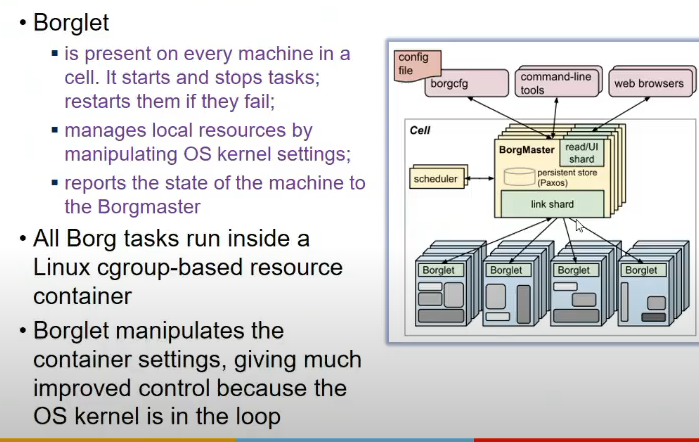
Borglet
- software running on each machine
- starts and stops a job
Workload Characteristics
- long running services
- should nvr go down
- very less latency
- batch jobs


- production and batch jobs
- production = latency sensitive
- batch = lower priority
Clusters and cells

- user submits jobs to borg mgr
- baki borg master dekhta
- kaha run karu
- kitne resources du
- kya dependencies hai, install kar usko
- monitor machines if fail, etc
Jobs and Tasks
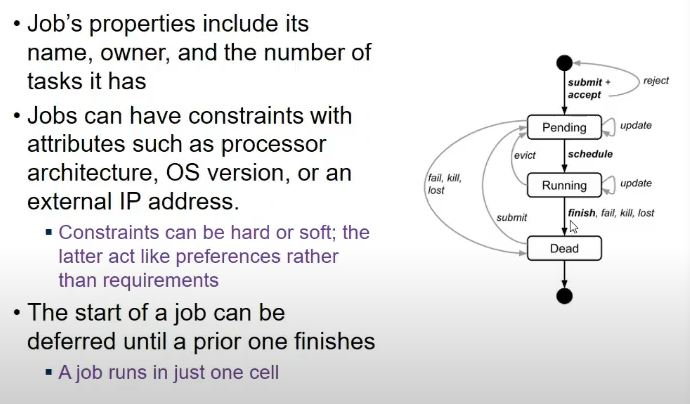
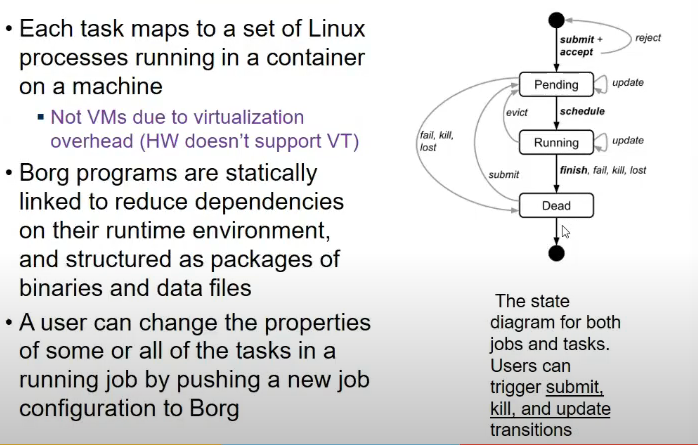
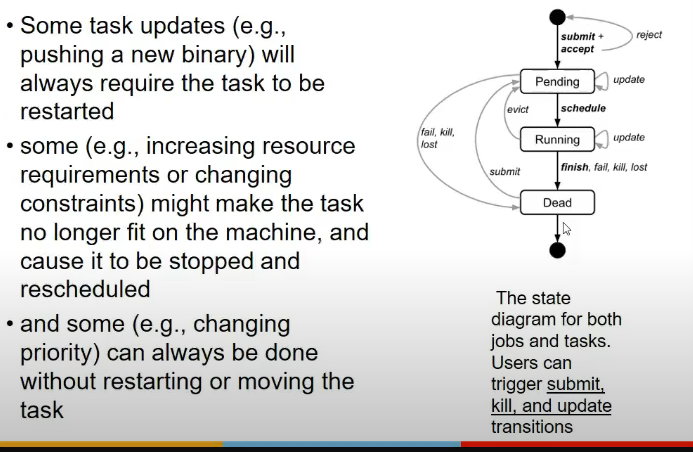
Priority, quota and admission control
- every job has a priority
- high priority can preempt lower priority for resources
- preemption cascades ho sakte
- solution: same band wale nahi preempt kar sakte
- ands
- monitoring>production>batch>best effort(aka testing/free)

Naming and Monitoring

Scheduling
