Lecture 3
- Lecture 3
Video
Slides
What is Cloud computing
- before cloud computing existed, Software as a service was still existing
- what makes cloud computing -

- provides illusion of infinite resources
- as and when necessary, I will take more servers/resources
- I do not have to predict max demand already
- Commitment required by cloud users (who use the services)
- ability to pay for use of resources on short term basis as needed
- abhi liye, and thodi der me returned
- provides illusion of infinite resources
- eg

- pehle wale failed bcz I need to negotiate and sign contract and all
- but successful wale
- billing is per hour basis or less
- scalable storage service (S3)
- no contract and all
- bandwidth charges are very less as well
- How these services are offered so cheaply
- when u do at big scale, u can do at cheap rate - economies of scale
- u can make multiple instances into single box
- put multiple instances as virtual boxes/containers into single box - statistical multiplexing
- bulkpurchasing
- discount jyada when u order things in bulk - eg
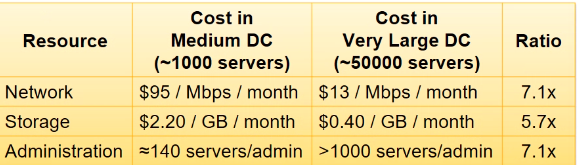
- discount jyada when u order things in bulk - eg
- is it possible for small scale company to provide cloud services
- Amazon toh kar sakta
- they have s/w stack to manage huge setup
- and infrastructure as well
- they extended it to public
- utilized off-peak capacity
- rented things they were not using
- Microsoft
- had lot of consumer base who used office suite and .NET products
- it just moved them to cloud
- Google
- had large setup and s/w stack
- used that to offer cloud services
- Amazon toh kar sakta
Economics of Cloud users
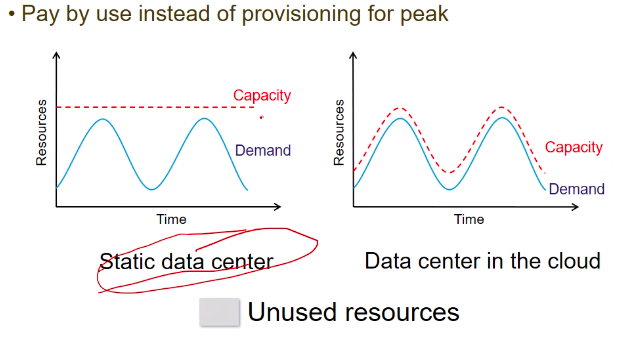
- u cannot give up capacity in static data center tho demand is varying
- increases cost
- Cloud side - resources are changing according to demand
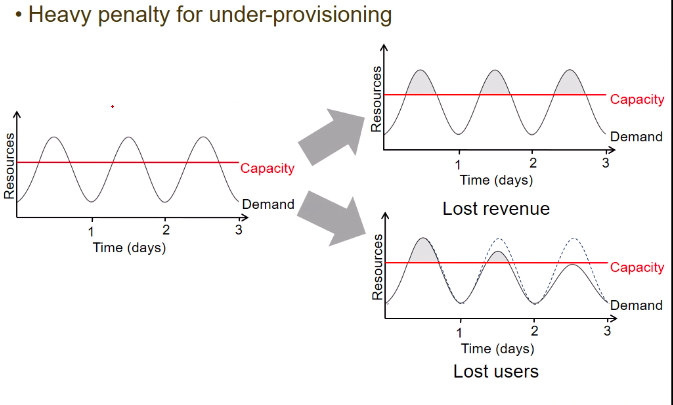
- when I have undercapacity, I will be dropping requests which exceed the capacity
- so I will lose confidence of users, demand will decrease (see 2nd graph)
- so ppl prefer cloud computing as a platform
Costs involved
Consumer point of view
- cap-ex = capital investment
- traditional
- one time investment
- acquiring space, firewalls, network equipments, air conditioning
- cloud
- not applicable
- I am not purchasing anyth 1-time, I am renting
- traditional
- op-ex
- traditional
- operational expenses
- electricity
- infrastructure wear and tear
- operational expenses
- cloud
- rental
- traditional
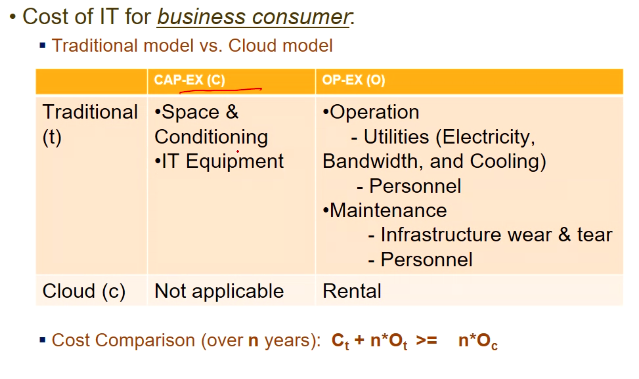
Provider point of view

- multi-tenancy
- m consumers will be using ur system simult maybe
- m se multiple nahi kia but function of m
- function will be sublinear
- I am multiplexing
- I will have some metadata corresponding to each customer
-
summing up costs , it should be less than total paisa consumers pay, tbhi profit hoga na bhai
- Analogies
- hotels
- multiple ppl check-in/check-out
- one room shared by multiple ppl
- time-share/vacation homes
- hotels
Definition of Cloud computing
Attributes of cloud computing
- 5 attributes

- resource pooling
- multiple consumers can access the resources
- provider’s resources are pooled
- location of resource is not reqd to be known by consumer

Cloud Computing
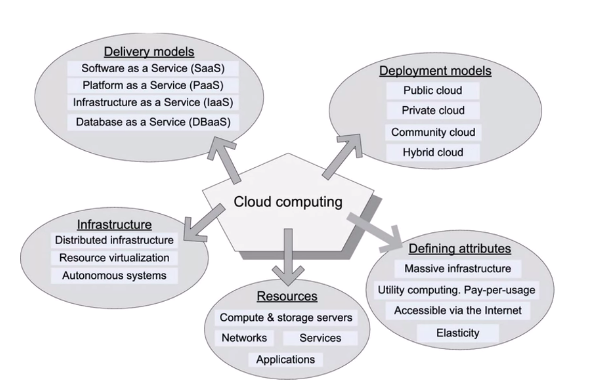
- deployment models
- community cloud
- gp of companies together using a cloud
- hybrid
- combn of public and private
- community cloud
- Delivery models
- SaaS - software
- PaaS - platform
- IaaS - infrastructure
- DaaS - database
Programming models in cloud
Outline
- Cloud applications
- Parallel Programming paradigms
- pleasingly synchronous model
- bulk synchronous model
- hadoop
Cloud applications
- pipelined exec
- batch processing apps
- offline data
- real time processing apps
- streaming data
- web apps
Data streams

- streams = continuous generation of data
- items come 1 by one, and are timestamped
- 2 challenges
- very fast
- processing of one item must finish before other arrives
- then only we can do without loosing buffer and all
- processing of one item must finish before other arrives
- and very large
- it’s unlimited stream
- very fast
- we need to extract info realtime
- cannot store everything at one place and then apply algos
- also, data might be evolving
- so models which I build, should adapt to change in data
Data flow mgmt in streaming algos
Distributed data flows
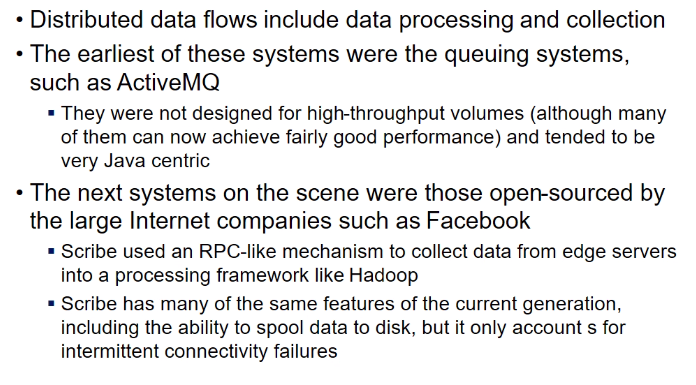
- ActiveMQ
- a queuing system
- generator can put stream into queue and reach destn
- scaling up is prob
- Scribe
- open-sourced by FB
- pools data and stores into disk
- Flume and Kafka
- recent open source systems
- meant for distributed collection of data
- follow publish/subscribe model
