Semester7
Notes of courses done/attended in semester 7 in college
Lecture 5
Video
link)
Summary
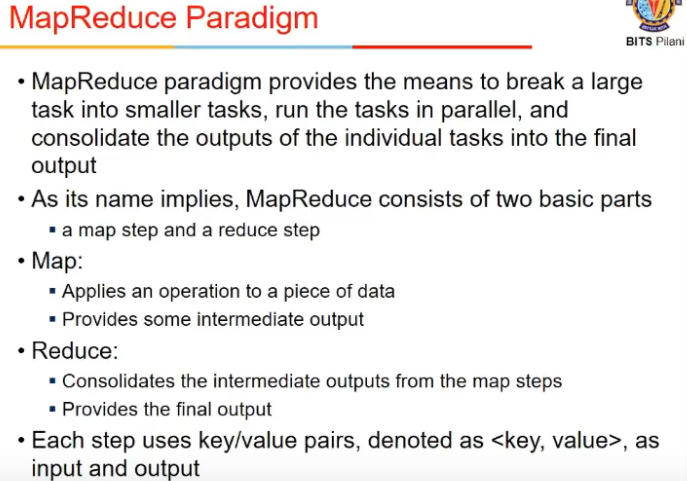
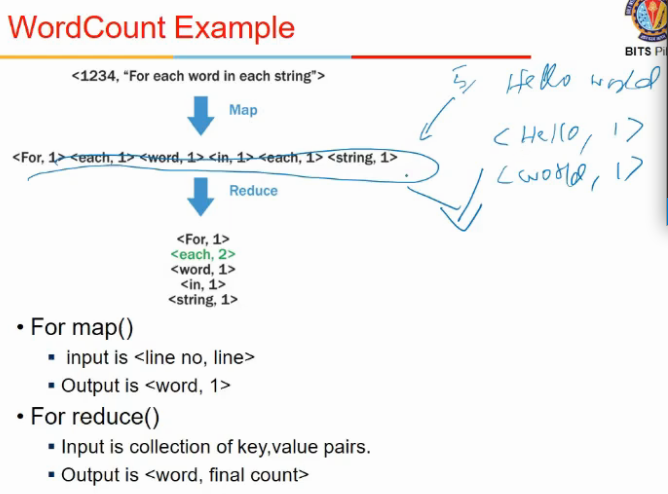
- map is executed for every record in database
- it outputs a (key, value) pair
- there is a middleware between map and reduce, which does shuffle and sort
- it takes output of map and sorts them locally, sends to a particular reducer
- one key goes to one reducer only, key is not split across reducers
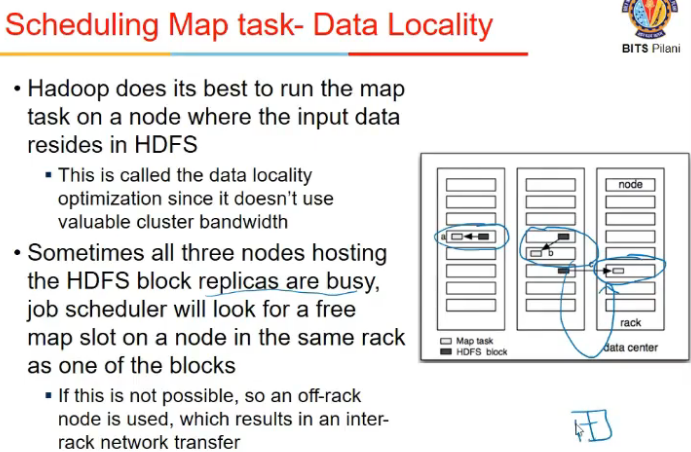
- data locality is followed so that #movements are minimized
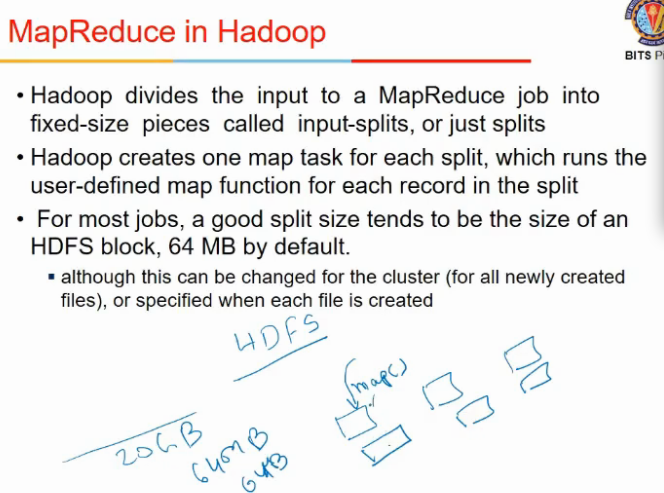
- #map jobs = # input chunks to avoid moving data
Scheduling in Hadoop
Map jobs
Reduce jobs

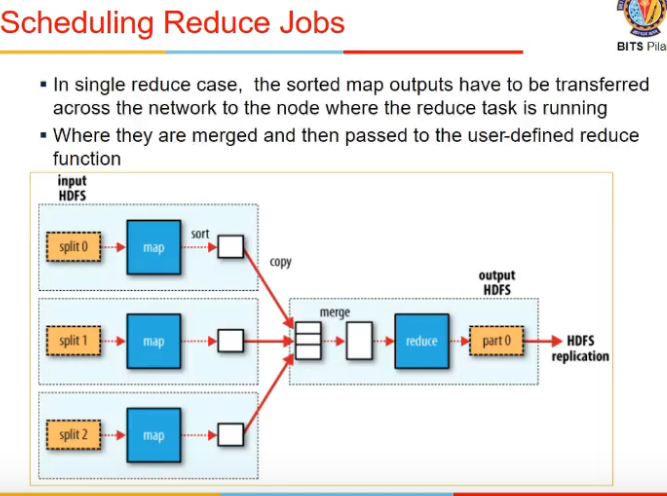
Multiple Reducers

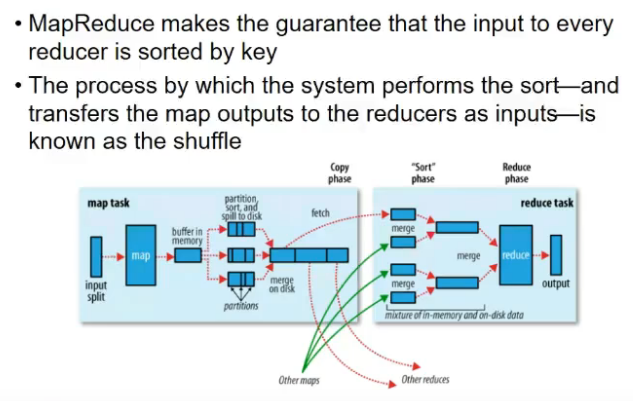
Shuffle and sort
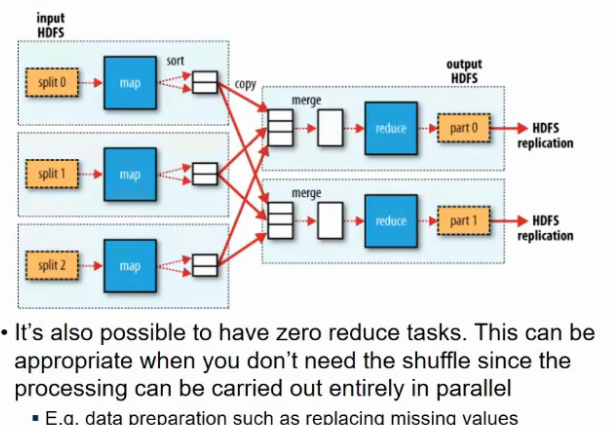
Data flow with multiple reduce tasks
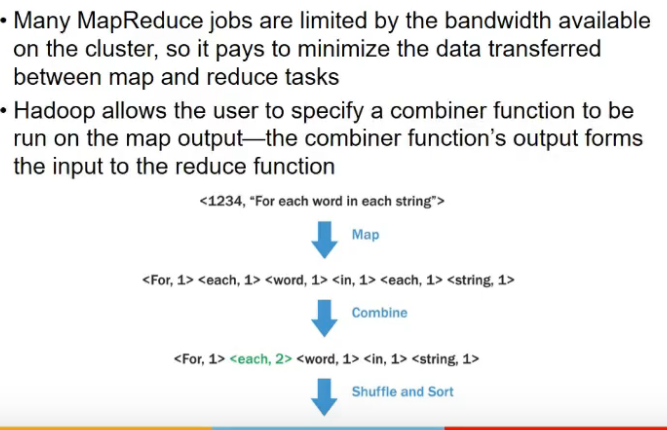
Combiner functions
MapReduce Example
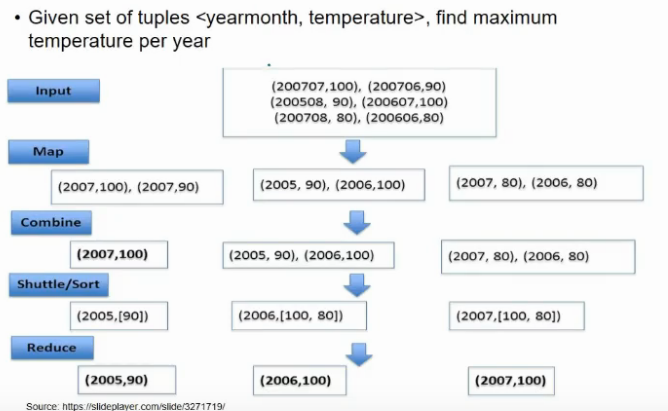
Chaining MapReduce Jobs

- cannot be done via a single mapreduce
- I might need 2 mapredyces
- first will find for each year, max avg temp
- this is input to second mapreduce
- it has to output top 5
- for 2nd map, key will be a dummy value : all elems will have same key
- and value will be <year, temp>
- sari keys go to 1 reducer
- it will give top 5
Joining data from different sources

- I need additional data which is not with me, I might need to take it from file and file might not be with me, since Hadoop me file bati hoti na
- there are high level frameworks for it
- pig
- hive
- like a SQL language for Hadoop
- u write a query
- query is converted into MapReduce queries internally
References
- Hadoop: The Definitive Guide, 4th Edition [Book] - O’Reilly Media












